Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(5), p.133 - 137, 2022/05
The effect of the corrosion inhibitor on the corrosion of steel under a thin solution layer was investigated. As a result of forming a thin solution layer with a thickness of 1.0-0.2 mm on the specimen, adding a mixed solution of sodium molybdate and aluminum lactate as a corrosion inhibitor, and performing electrochemical measurement, the corrosion inhibitor suppresses the anodic reaction. And in the thin solution layer, it was suggested that the morphology of the protective layer structure by the corrosion inhibitor changed according to the amount of liquid as compared with the bulk immersion.
Yasuda, Satoshi; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Kato, Masaru*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yagi, Ichizo*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 125(40), p.22154 - 22162, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:57.69(Chemistry, Physical)Understanding electrochemical behavior of the alkaline metal cation-graphene interface in electrolyte is essential for understanding the fundamental electrochemical interface and development of graphene-based technologies. We report comprehensive analysis of the electrochemical behavior of both alkaline metal cations and graphene using electrochemical surface X-ray diffraction (EC-SXRD) and Raman (EC-Raman) spectroscopic techniques in which the interfacial structure of cations and the charging state and mechanical strain of the graphene can be elucidated. EC-SXRD and cyclic voltammetry demonstrated electrochemically driven specific adsorption and desorption of cations on the graphene surface involved in the dehydration and hydration process. This study provides new insight for understanding fundamental electrochemical behavior of the alkaline metal cation-graphene interface and contributes to the development of carbon-based novel applications.
Kanamura, Shohei*; Takahashi, Yuya*; Omori, Takashi*; Nohira, Toshiyuki*; Sakamura, Yoshiharu*; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Denki Kagaku, 88(3), p.289 - 290, 2020/09
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Masahiro
Keisan Kogaku, 25(3), p.4105 - 4108, 2020/07
Recently, some attempts using Multi-Physics simulation for corrosion problems, especially crevice corrosion, have been increasing. Corrosion undergoes by electrochemical reaction. The numerical calculation procedure is used a non-liner equation. Furthermore, this reaction is affected by environmental factors, i.e. composition, amount and mobility of chemical species and redox potential. These values change with time by corrosion process itself. This report, these needs for Multi-Physics calculations are introduced.
Yasuda, Satoshi; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Terasawa, Tomoo; Yano, Masahiro; Nakajima, Hideaki*; Morimoto, Takahiro*; Okazaki, Toshiya*; Agari, Ryushi*; Takahashi, Yasufumi*; Kato, Masaru*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 124(9), p.5300 - 5307, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:60.14(Chemistry, Physical)Confinement of hydrogen molecules at graphene-substrate interface has presented significant importance from the viewpoints of development of fundamental understanding of two-dimensional material interface and energy storage system. In this study, we investigate H confinement at a graphene-Au interface by combining selective proton permeability of graphene and the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (electrochemical HER) method. After HER on a graphene/Au electrode in protonic acidic solution, scanning tunneling microscopy finds that H
confinement at a graphene-Au interface by combining selective proton permeability of graphene and the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (electrochemical HER) method. After HER on a graphene/Au electrode in protonic acidic solution, scanning tunneling microscopy finds that H nanobubble structures can be produced between graphene and the Au surface. Strain analysis by Raman spectroscopy also shows that atomic size roughness on the graphene/Au surface originating from the HER-induced strain relaxation of graphene plays significant role in formation of the nucleation site and H
nanobubble structures can be produced between graphene and the Au surface. Strain analysis by Raman spectroscopy also shows that atomic size roughness on the graphene/Au surface originating from the HER-induced strain relaxation of graphene plays significant role in formation of the nucleation site and H storage capacity.
storage capacity.
Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Cagnes, M.*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Kanaya, Toshiji*; Darwish, T. A.*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 21(32), p.17512 - 17516, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:53.26(Chemistry, Physical)We combined the deuterium labeling and neutron reflectivity techniques to determine the fine structure of the electric double layer structure in an imidazolium ionic liquid (IL). For this, a simple and large scale deuteration method for imidazolium ILs was developed, where the deuteration level can be systematically controlled.
Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 68(1), p.2 - 8, 2019/01
It is important to control the cooling water of light water reactors (boiling water reactor and pressurized water reactor) to suitable quality in order to reduce corrosion of structural materials and generation of radioactive corrosion products. For that purpose, monitoring of water quality using electrochemical measurement method is necessary. In this article, the application of ECP measurement to BWR is mainly focused, I describe the water quality of light water reactors and the necessity of electrochemical measurement.
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Radioisotopes, 67(10), p.483 - 493, 2018/10
Electrochemical reactions and redox properties of actinides such as uranium and neptunium are outlined. The flow electrolysis enables rapid and high-efficient treatment. It was demonstrated to measure slow processes of actinide redox. Experimental results of electrolysis of actinide ions and the preparation method of oxidation state of the ions based on the fundamental data are described. Mediator reaction and catalysis observed in the process of electrolysis of actinide ions are also explained.
Yamamoto, Masahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo 2016 Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.1 - 8, 2016/05
I will make a presentation for "Go Okamoto Memorial Lecture" at coming Zairyo to Kankyo 2016 Symposium. I will introduce the data analysis method using reproducing experiment for an actual environment. The examples will be shown in case of maritime structure and nuclear engineering plant.
 , and NaCO
, and NaCO solutions
solutionsUehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Yamana, Hajimu*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Radiochimica Acta, 104(1), p.1 - 9, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The spectroelectrochemical cell was fabricated for in-situ X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurement. The XAFS spectra of U L -edge were monitored in electrolyte solutions during the electrochemical reduction. Tetravalent uranium was electrochemically prepared from hexavalent uranium and the extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) was analyzed. The U
-edge were monitored in electrolyte solutions during the electrochemical reduction. Tetravalent uranium was electrochemically prepared from hexavalent uranium and the extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) was analyzed. The U formed in 0.1M HNO
formed in 0.1M HNO was partially re-oxidized to UO
was partially re-oxidized to UO
 by NO
by NO
 in the solution. The UO
in the solution. The UO
 carbonates were prepared during electrolysis.
carbonates were prepared during electrolysis.
Aoki, So; Taniguchi, Tomomi*; Sakai, Junichi*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 64(9), p.414 - 420, 2015/09
The objective of this study is to clarify the preferential dissolution mechanism of a duplex stainless steel (DSS) at its corrosion potential by means of in-situ Scanning Electrochemical Microscope observation. Probe electrode was fixed above ferritic and austenitic each phase of DSS at corrosion potential. Potential of the probe electrode was polarized toward noble direction, and probe current was measured. In a probe potential range of 0-0.70 V (SHE), anodic current due to hydrogen oxidation reaction could be detected. This anodic current was larger above austenitic phase than that above ferritic phase. In a probe potential range of 0.70-1.2 V, anodic current due to Fe oxidation reaction to Fe
oxidation reaction to Fe could be detected. This anodic current was larger above ferritic phase than that above austenitic phase. Based on these results, a preferential dissolution mechanism model of a DSS at the corrosion potential is proposed using internal polarization curves.
could be detected. This anodic current was larger above ferritic phase than that above austenitic phase. Based on these results, a preferential dissolution mechanism model of a DSS at the corrosion potential is proposed using internal polarization curves.
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki, 2015(6), p.239 - 244, 2015/06
Electrochemical studies of ion transfer and charge transfer at liquid/liquid interface reported between 2012 and 2014 were surveyed. They were categorized by method of measurement. The merit of the method, improvement, species of application were described. Applied research such as analyses of redox inactive species, sensitive analyses based on adsorption at the interface and developments of new functional materials had been widely carried out.
Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 64(3), p.91 - 97, 2015/03
In the boiling water reactors (BWRs), reactor cooling water is maintained in high purity condition by controlling of a deionizing and deaerating apparatus, however H O
O contains by water radiolysis. In order to determine the corrosive condition in high-temperature pure water containing H
contains by water radiolysis. In order to determine the corrosive condition in high-temperature pure water containing H O
O , the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was performed in this study. To simulate BWR condition precisely, the measurements were performed without any electrolyte. The obtained impedance responses were changed with the H
, the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was performed in this study. To simulate BWR condition precisely, the measurements were performed without any electrolyte. The obtained impedance responses were changed with the H O
O concentration. The solution resistance and polarization resistance were determined by the equivalent circuit analyses. The conductivity was determined by the obtained solution resistance and the calculation of the current flow between the working electrode and the counter electrode by the 3-demensional finite element method. The value, 4.4
concentration. The solution resistance and polarization resistance were determined by the equivalent circuit analyses. The conductivity was determined by the obtained solution resistance and the calculation of the current flow between the working electrode and the counter electrode by the 3-demensional finite element method. The value, 4.4 10
10 S/cm, was obtained as the conductivity of the pure water at 288
S/cm, was obtained as the conductivity of the pure water at 288 C. The reciprocal of the obtained polarization resistance increased in proportion with H
C. The reciprocal of the obtained polarization resistance increased in proportion with H O
O concentration. This indicates that the corrosion current density was determined by the diffusion limiting current density of H
concentration. This indicates that the corrosion current density was determined by the diffusion limiting current density of H O
O . The diffusion coefficient of H
. The diffusion coefficient of H O
O at 288
at 288 C was determined using the relationship between the reciprocal of the polarization resistance and H
C was determined using the relationship between the reciprocal of the polarization resistance and H O
O concentration. The obtained diffusion coefficient was 1.5
concentration. The obtained diffusion coefficient was 1.5 10
10 cm
cm /s. This is about twice larger than that of the reported value of O
/s. This is about twice larger than that of the reported value of O .
.
Shirai, Osamu*; Yamana, Hajimu*; Arai, Yasuo
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1267 - 1273, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:84.47(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 2) and (
2) and (

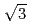 ) structures using surface X-ray diffraction
) structures using surface X-ray diffractionTamura, Kazuhisa; Mizuki, Junichiro
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 109(26), p.12832 - 12836, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:4.61(Chemistry, Physical)The kinetics of the phase transition between the (2  2) and (
2) and (

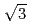 )-Bi structures on Au(111) was investigated using electrochemical methods and time-resolved surface X-ray diffraction. The temporal changes in the current value and the diffracted X-ray intensity that originated from the (2
)-Bi structures on Au(111) was investigated using electrochemical methods and time-resolved surface X-ray diffraction. The temporal changes in the current value and the diffracted X-ray intensity that originated from the (2  2)-Bi overlayer were monitored during the phase transitions at various overpotentials. For the (
2)-Bi overlayer were monitored during the phase transitions at various overpotentials. For the (

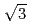 )
)  (2
(2  2) phase transition, the phase transition models determined by the X-ray and electrochemical measurements were a surface-diffusion controlled instantaneous nucleation-growth process and a Langmuir process, respectively. For the reverse transition, the phase transition models determined by X-ray and electrochemical measurements were a Langmuir adsorption process and a surface diffusion controlled nucleation-growth process, respectively.
2) phase transition, the phase transition models determined by the X-ray and electrochemical measurements were a surface-diffusion controlled instantaneous nucleation-growth process and a Langmuir process, respectively. For the reverse transition, the phase transition models determined by X-ray and electrochemical measurements were a Langmuir adsorption process and a surface diffusion controlled nucleation-growth process, respectively.
 films electroplated to stainless steel substrates
films electroplated to stainless steel substratesAbe, Hideki*; Nishida, Kenji*; Imai, Motoharu*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Yoshii, Kenji
Applied Physics Letters, 85(25), p.6197 - 6199, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:51.46(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Shiina, Yasuaki; Takizuka, Takakazu; Kasahara, Seiji
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 46(12), p.862 - 863, 2004/12
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Minato, Kazuo
JAERI-Conf 2004-008, 228 Pages, 2004/04
Applications of molten salts technology to separation and synthesis of materials have a potential to give us a civilized life, for example aluminium refinement. Recently, much attention is given to the pyrochemical reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels in the molten salt research field. On the other hand, computer simulation technique is expected to play an important role for supporting experimental works and predicting unknown physical properties in the molten salts application studies. Research group for Actinides Science, Department of Materials Science, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute(JAERI), together with Reprocessing and Recycle Technology Division, Atomic Energy Society of Japan, organized the 3rd Workshop on Molten Salts Technology and Computer Simulation at Tokai Research Establishment, JAERI on December 16, 2003. Many molten salts researchers in Japan participated in the workshop and many useful presentations and discussions were performed.
Takahashi, Masamitsu
Denki Kagaku Oyobi Kogyo Butsuri Kagaku, 72(2), p.128 - 132, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Kawamura, Yoshinori; Konishi, Satoshi; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Science and Technology, 45(1), p.33 - 40, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:81.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)Aiming at realization of the efficient blanket tritium recovery system of a fusion reactor, research and development of the hydrogen pump using the proton conductor are furthered. One of the advantages of the system using the hydrogen pump is concurrent processing of hydrogen isotopes and water vapor by one component. In this work, experimental research on the hydrogen extraction characteristic in a water molecule was performed with the hydrogen pump using SrCe Yb
Yb O
O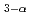 . In hydrogen extraction from a water molecule, application of the threshold, voltage corresponding to the decomposition energy of water, is necessary. The observed threshold was about 500-600mV at 873K and decreased with the increase in water vapor pressure. About pumping of H
. In hydrogen extraction from a water molecule, application of the threshold, voltage corresponding to the decomposition energy of water, is necessary. The observed threshold was about 500-600mV at 873K and decreased with the increase in water vapor pressure. About pumping of H -H
-H O mixture gas, the permeation of H
O mixture gas, the permeation of H anteceded water decomposition, and the threshold of water decomposition increased with the increase in hydrogen partial pressure. In order to process concurrently, application of fairly higher voltage is expected to be necessary.
anteceded water decomposition, and the threshold of water decomposition increased with the increase in hydrogen partial pressure. In order to process concurrently, application of fairly higher voltage is expected to be necessary.